NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
Here you will find NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System will develop the ability to effectively respond to the high end questions that you’re confronted with. Detailed explanation provided under each NCERT solutions will help in understanding the concepts better. It will allow students to cover the entire syllabus effectively without any frustration.
NCERT Solutions for Science prepared by our experts try to provide all round clarity of questions. Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Class 8 Science NCERT Questions and Answers will improve application skills and clear your confusions. It can be used to enrich knowledge and make lessons for learners more exciting.

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
This NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 are helpful resources that can help you not only cover the entire syllabus but also provide in depth analysis of the topics. Your marks play an important role in shaping future thus these NCERT Solutions will become your comprehensive guide in easy learning and evaluating yourself. In the examinations, you will can come up with better answers and lay out the main point effectively.
| Study Material for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System |
|---|
|
Exercises
1. Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
(a) An asteroid
(b) A satellite
(c) A constellation
(d) A comet
► (c) A constellation
2. Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
(a) Sirius
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Earth
► (a) Sirius
3. Phases of the moon occur because
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) our distance from the moon keeps changing.
(c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon's surface.
(d) the thickness of the moon's atmosphere is not constant.
► (a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
4. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The planet which is farthest from the sun is _________.
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is _________.
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a __ _________.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as a_________.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not _________.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of __________ and _________.
Answer
(a) The planet which is farthest from the sun is Neptune.
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is Mars.
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a constellation.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as a satellite.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not stars.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
5. Mark the following statement as true (T) or false (F).
(a) Pole star is a member of the solar system. ( )
► False
(b) Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system. ( )
► True
(c) Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. ( )
► False
(d) INSAT is an artificial satellite. ( )
► True
(e) There are nine planets in the solar system. ( )
► False
(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( )
► False(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ( )
Page No: 235
6. Match items in column A with one or more items in column B.
A
|
B
|
||
| (i) | Inner planets | (a) | Saturn |
| (ii) | Outer planets | (b) | Pole star |
| (iii) | Constellation | (c) | Great Bear |
| (iv) | Satellite of the Earth | (d) | Moon |
| (e) | Earth | ||
| (f) | Orion | ||
| (g) | Mars | ||
Answer
A
|
B
|
||
| (i) | Inner planets | (g), (e) | Mars, Earth |
| (ii) | Outer planets | (a) | Saturn |
| (iii) | Constellation | (c), (f) | Great Bear, Orion |
| (iv) | Satellite of the Earth | (d) | Moon |
7. In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer
Venus appears in the western sky after sunset and is called the evening star.
8. Name the largest planet of the solar system.
► Jupiter
9. What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer
A constellation is a group of stars that form a recognisable pattern in the sky.
The two constellations name are Ursa Major and Orion.
10. Draw sketches to show the relative position of prominent stars in (a) Ursa Major and (b) Orion.
Answer
(a) Ursa Major appears like a big dipper. There are three bright stars in the handle and four stars in the bowl of the dipper as shown in below figure.
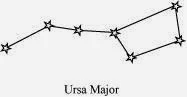

Answer
Page No: 237
12. Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer
The pole star can be located using the ursa major constellation, by imagining a line towards the Northern direction connecting two stars present at the end of the bowl, This imaginary line meets Pole Star. The length of the imaginary line from the bowl is about five times the distance between the two stars of the bowl.

Answer
No, Stars do not move they actually appear to move from east to west due to rotation of earth on its axis from west to east.
14. Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years away from the Earth?
Answer
A star is located eight light years away from the Earth. This means that the distance between the star and the Earth is equivalent to the distance travelled by light in eight years, i.e., a star is located 8 x (9.46 x 1012) = 7.6 x 1013km away from the Earth.
15. The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer
Earth and Jupiter can be considered as two spheres with radii R and R' respectively. Given that the radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth.
Thus, R' = 11 R

16. Boojho made the following sketch (Fig. 17.29) of the solar system. Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.

Answer
No, the sketch is not correct as the planet because he has interchanged the positions of Mars and Venus and also the positions of Uranus and Neptune. Also, he has shown the Asteroid belt in the gap between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn which is not correct. The asteroid belt is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The correct fig is given below.

Go Back To NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions
Given NCERT Solutions are available in understandable language in order to be effective and perform better in the class. You will develop the ability to identify what improvements and changes need to be made. Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 17 is an effective method for learning since you can be le to learn a lot within a short time.
Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System NCERT Questions and Answers - Topics
• The Moon
→ The Moon’s Surface
• The Stars
• Constellations
• The Solar System
→ The Sun
→ The Planets
• Some Other Members of the Solar System
→ Asteroids
→ Comets
→ Meteors and Meteorites
→ Artificial Satellites
Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - Notes
• The stars, the planets, the moon and many other objects in the sky are called celestial objects.
• The study of celestial objects and associated phenomena is called astronomy.
• The moon is a natural satellite of the earth.
→ When the moon is positioned between the sun and the earth, the illuminated portion of the moon is away from the earth, and we are not able to see the moon. We call this day as the 'new moon day'.
→ With time, the position of the moon changes and the illuminated portion of the moon exposed to the earth gradually increases. Thus, the size of the apparent disc of the moon increases gradually from a crescent to a full round when the earth lies between the moon and the sun. We call this day the 'full moon day'.
→ The various shapes of the bright part of the moon as seen during a month are called phases of the moon.
→ The moon has no atmosphere. It has no water.
• The stars emit light of their own. The Sun is also a star.
→ The stars are millions of times farther away than the Sun. Therefore, the stars appear to us like points.
→ Large distances are expressed in another unit known as light year. It is the distance travelled by light in one year. The speed of light is about 300,000 km per second. The Sun is nearly 150,000,000 kilometres (150 million km) away from the Earth.
• The stars forming a group that has a recognisable shape is called a constellation.
→ One of the most famous constellations which you can see during summer time in the early part of the
night is Ursa Major. It is also known as the Big Dipper, the Great Bear or the Saptarshi. There are seven prominent stars in this constellation. It appears like a big ladle or a question mark.
→ Orion is another well-known constellation that can be seen during winter in the late evenings.
→ Cassiopeia is another prominent constellation in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night. It looks like a distorted letter W or M.
• The Sun and the celestial bodies which revolve around it form the solar system. It consists of large number of bodies such as planets, comets, asteroids and meteors.
→ The eight planets in their order of distance from the Sun are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars,
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
→ The Sun is the nearest star from us. It is continuously emitting huge amounts of heat and light. The Sun is the source of almost all energy on the Earth.
→ A planet has a definite path in which it revolves around the Sun. This path is called an orbit. The time taken by a planet to complete one revolution is called its period of revolution.
→ The planet mercury is nearest to the Sun. It is the smallest planet of our solar system.
→ Venus is earth’s nearest planetary neighbour. It is the brightest planet in the night sky.
→ The Earth is the only planet in the solar system on which life is known to exist. From space, the Earth appears blue-green due to the reflection of light from water and landmass on its surface.
→ The Mars slightly reddish and, therefore, it is also called the red planet. It has two small natural satellites.
→ Jupiter is the largest planet of the solar system. Jupiter has a large number of satellites. It also has faint rings around it.
→ Saturn appears yellowish in colour and has beautiful rings. These rings are not visible with the naked eye. It also has a large number of satellites.
→ Uranus and Neptune are the outermost planets of the solar system. They can be seen only with the help of large telescopes.
→ The first four planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called the inner planets while Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are called the outer planets. They have a ring system around them.
• The large gap in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter is occupied by a large number of small objects that revolve around the Sun which are called asteroids.
• Comets revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. However, their period of revolution round the Sun is usually very long.
• A meteor is usually a small object that occasionally enters the earth’s atmosphere. Some meteors are large and so they can reach the Earth before they evaporate completely. The body that reaches the Earth is called a meteorite.
• Artificial satellites are man-made. They are launched from the Earth. They revolve around the Earth much closer than earth’s natural satellite, the moon.
→ Aryabhata was the first Indian satellite. Some other Indian satellites are INSAT, IRS, Kalpana-1, EDUSAT, etc.
→ These satellites are used for forecasting weather, transmitting television, radio signals, telecommunication and remote sensing.
Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Class 8 Science Questions and Answers - MCQ Questions with answers
1. How do stars appear to move?
a) From east to west
b) From west to east
c) From north to south
d) From south to north
► a) From east to west
2. The stars, planets, moon and objects in sky are called
a) Solar system
b) Celestial bodies
c) Natural bodies
d) Lunar bodies
► b) Celestial bodies
3. The tilting of the earth is responsible for
a) change of days
b) change of the sun’s rays
c) change of season
d) none of the above
► c) change of season
4. Which of the following physical quantities has light year as its unit?
a) Time
b) Intensity of light
c) Illumination
d) Distance
► d) Distance
5. The path of planet around the sun is called its
a) Orbit
b) Spin
c) Rotation
d) Revolution
► a) Orbit
6. The brightest object in clear night sky is
a) Venus
b) Sun
c) Moon
d) Star
► c) Moon
7. Size of moon keeps changing when viewed from earth. This change is called
a) Phases of moon
b) Lunar eclipse
c) Solar eclipse
d) Segment of moon
► a) Phases of moon
8. Moon is the
a) Natural satellite of Earth
b) Artificial satellite of Earth
c) Largest star of solar system
d) Nearest star of solar system
► a) Natural satellite of Earth
9. The sun makes life possible by providing us with
a) Oxygen
b) Water
c) Heat and light
d) Carbon dioxide
► c) Heat and light
10. Which of the following is not a planet?
a) Mercury
b) Moon
c) Saturn
d) Mars
► b) Moon
Through these NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17, students should not waste time and adopt a strategy that helps them operate and learn at maximum efficiency. It will help in developing a wider body of knowledge when you’re brainstorming a solution. Students should also refer previous year questions and practise test papers and worksheets to assess their key areas.
