Study Material and Notes of Chapter 4 Introduction to HTML Computer Science Class 9th
• HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language.
Overview of HTML
• Who Invented HTML: HTML was invented in November 1990 by a scientist called Tim Berneses-Lee.
• Tools needed to get started with HTML documents:
→ A tag is a special word enclosed in angle-brackets < >. It tells the browser to perform an action as asked by the special word.
→ A text editor/HTML editor
→ A Web Browser
• Tags and attributes
→ The characteristics or the features of a tag are defined by an attribute. An attribute is used
inside a tag which always takes a value to help the browser perform the specific task in a particular direction.
→ An element is a combination of a start tag, the text and the end tag.
For example: <body> element begins with start tag, followed by text and ends with end tag.</body>
• Container of Tags: One set of tags may contain another set of tags. This is called nesting
of tags. For example: <TAG1> <TAG2>……………</TAG2> </TAG1>.
Here, <TAG1> and </TAG1> is the first block of tags. <TAG2> and </TAG2> is the second block of tags.
Structure of HTML document
• Basic structure of HTML document is:

• The basic structure of the HTML document is divided into two sections namely, the head and the body.
→ The first section helps in changing the heading on the title bar of the HTML document (the webpage).
→ The second section begins with the start tag of BODY. The data on the webpage is displayed through the tags used in this section.
Saving the HTML document
• After writing HTML code, click on File menu and select Save option. A window open asking o save the file in a folder. Give a name and an extension to the file. The extension in this file will be .html or .htm. which will turn the file into a webpage.
• To modify the webpage, either open the web page and click on View →source or open the webpage with notepad.
Container and empty tags
• A container tag has both the start and the end tag. The text or the graphic is inserted inside the beginning and end tag of the container tag. For example: <body>This is a container tag</body>. The <BODY> tag here is a container tag which has both the beginning and the ending tag and the text in between both the tags.
• The empty tag is a stand-alone tag. This implies that such a tag has beginning but no ending tag. For example: The <BR> tag is used for adding one line break.
→ Other empty tags are HR tag, Comment tag.
BODY tag
• The second section of the webpage begins with the <BODY> tag. This defines the visible section of the document.
• It has a number of attributes which controls the overall appearance of the document. Below is the list of attributes of the <BODY> tag:

Formatting Elements
• There are a number of tags that help you to format the text.
• <Heading tags>: It is used to display the heading or the main topic on the web page. This tag varies from H1 to H6.
→ This is a container tag.
→ The font size of headings decreases with the increase in the number of heading tag.
→ The <H1> tag shows the heading with the largest font size while <H6> tag shows the heading with the smallest font size.
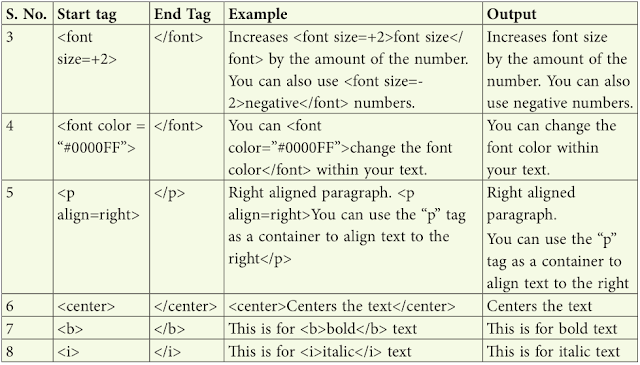
• <FONT> tag: The FONT tag is a container tag that has a number of attributes given in the table.

• Entering Paragraph text on your Web page: A paragraph can be written on the web document using the <p> tag. This is a container tag, though the </p> tag is optional.
→ It uses one attribute called align that takes the value left, right or center.
• The Center tag: It places the text in the center. Sometimes it may not be possible to use align
attribute again and again along with a tag. Then it is better to use nested form of center
tag once and use other tags inside the opening and closing center tags.
• Bold, Italics and Underline: There are other tag that help in changing the style of the font.
→ <B> , </B> : used for making bold text.
→ <I> , </I> : used for making italic text.
→ <U> , </U>: used for making underlined text.
Summary of all the tags used with their example and the output

NCERT Solutions of Ch 4 Introduction to HTML
inside a tag which always takes a value to help the browser perform the specific task in a particular direction.
→ An element is a combination of a start tag, the text and the end tag.
For example: <body> element begins with start tag, followed by text and ends with end tag.</body>
• Container of Tags: One set of tags may contain another set of tags. This is called nesting
of tags. For example: <TAG1> <TAG2>……………</TAG2> </TAG1>.
Here, <TAG1> and </TAG1> is the first block of tags. <TAG2> and </TAG2> is the second block of tags.
Structure of HTML document
• Basic structure of HTML document is:

• The basic structure of the HTML document is divided into two sections namely, the head and the body.
→ The first section helps in changing the heading on the title bar of the HTML document (the webpage).
→ The second section begins with the start tag of BODY. The data on the webpage is displayed through the tags used in this section.
Saving the HTML document
• After writing HTML code, click on File menu and select Save option. A window open asking o save the file in a folder. Give a name and an extension to the file. The extension in this file will be .html or .htm. which will turn the file into a webpage.
• To modify the webpage, either open the web page and click on View →source or open the webpage with notepad.
Container and empty tags
• A container tag has both the start and the end tag. The text or the graphic is inserted inside the beginning and end tag of the container tag. For example: <body>This is a container tag</body>. The <BODY> tag here is a container tag which has both the beginning and the ending tag and the text in between both the tags.
• The empty tag is a stand-alone tag. This implies that such a tag has beginning but no ending tag. For example: The <BR> tag is used for adding one line break.
→ Other empty tags are HR tag, Comment tag.
BODY tag
• The second section of the webpage begins with the <BODY> tag. This defines the visible section of the document.
• It has a number of attributes which controls the overall appearance of the document. Below is the list of attributes of the <BODY> tag:

Formatting Elements
• There are a number of tags that help you to format the text.
• <Heading tags>: It is used to display the heading or the main topic on the web page. This tag varies from H1 to H6.
→ This is a container tag.
→ The font size of headings decreases with the increase in the number of heading tag.
→ The <H1> tag shows the heading with the largest font size while <H6> tag shows the heading with the smallest font size.
• <FONT> tag: The FONT tag is a container tag that has a number of attributes given in the table.

• Entering Paragraph text on your Web page: A paragraph can be written on the web document using the <p> tag. This is a container tag, though the </p> tag is optional.
→ It uses one attribute called align that takes the value left, right or center.
• The Center tag: It places the text in the center. Sometimes it may not be possible to use align
attribute again and again along with a tag. Then it is better to use nested form of center
tag once and use other tags inside the opening and closing center tags.
• Bold, Italics and Underline: There are other tag that help in changing the style of the font.
→ <B> , </B> : used for making bold text.
→ <I> , </I> : used for making italic text.
→ <U> , </U>: used for making underlined text.
Summary of all the tags used with their example and the output


NCERT Solutions of Ch 4 Introduction to HTML

