Study Material and Notes of Ch 9 Reproduction in Animals Class 8th Science
Topics in the chapter
• Male Reproductive System
• Female Reproductive System
• Fertilization
→ Internal fertilization
→ External Fertilization
• Test tube baby
• Fertilization in Humans
• Asexual reproduction
→ Budding
→ Fission
→ Cloning
• Oviparous animals
• Viviparous animals
• Metamorphosis
• Lifecycle of silkworm
• Hormone responsible for metamorphosis in insects
Male Reproductive System
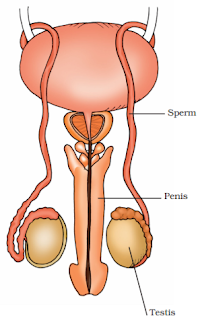
→ It consists of testis, sperm duct and penis.
→ Testes are involved in the production of male gametes called sperms.
→ Millions of sperms are produced by the testes.

→ Each sperm consists of three parts: Head, middle piece and tail.
Female reproductive system

→ It consists of ovaries, oviduct and uterus.
→ Ovaries produce ova or eggs.
→ A single matured egg is released from ovary into oviduct every month.
→ Baby develops in the uterus.
→ Egg is also single celled like sperm.
Fertilization

→ The process of fusion of male and female gametes (egg and sperm) to form zygote is known as fertilization.
→ It is of two types:
(i) Internal fertilization
(ii) External fertilization
Internal fertilization
→ In this, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place inside the female's body.
→ It occurs in cows, dogs and humans.
External fertilization
→ In this, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place outside the female's body in a surrounding medium, generally water.
→ It occurs in frogs, fishes, starfish, etc.
Test tube baby
→ A baby conceived by fertilization that occurs outside the mother’s body is called test tube baby.
→ Development of the embryo
→ The zygote repeatedly divides to form a ball of cells.
→ The ball of cells then starts differentiating into tissues and organs. At this stage, it is called embryo.
→ Embryo gets attached to the wall of the uterus and develops various body parts such as hands and legs.
→ Foetus is a stage of embryo that shows main recognizable feature of mature organism.
→ Foetus develops for nine months inside the mother’s womb and is finally delivered.
Fertilization in Humans

→ Fusion of the nucleus of the sperm with the ovum to form a zygote. It occurs in the fallopian tube of females.

→ Zygote divides to form an embryo.

→ Embryo is implanted in the uterus.

→ Foetus develops inside the mother’s body for nine months (gestation period).
Asexual reproduction
→ The type of reproduction which involves only a single parent and the new individuals are formed without the fusion of gametes is known as asexual reproduction.
• Three common methods of asexual reproduction are:
(i) Budding
(ii) Fission
(iii) Cloning
Budding
→ It involves the formation of new individual from the bulging of the parent body.

→ This phenomenon is very common in plants, fungi and animals such as Hydra and yeast.
Fission

→ Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction that occurs in Amoeba.
→ It is a type of asexual reproduction in which a single cell divides into two halves.
Cloning

→ Cloning is the process used to create an exact copy of a cell, tissue or an organism.
→ Dolly, a sheep was the first mammal to be cloned. It was cloned by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues in 1996.
Oviparous animals
→ The animals that lay eggs are called oviparous animals.

→ The examples include all kinds of birds, lizards, snakes, and frogs.
Viviparous animals
→ The animals that give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals.
→ The examples include cows, dogs, and humans.
Metamorphosis
→ The biological process of transformation of larva into an adult is known as metamorphosis.

• The life cycle of frog consists of the following stages:
Egg → Tadpole (larva) → Adult
→ Hormones controlling metamorphosis in frogs
→ Thyroxin (produced by the thyroid gland) initiates the process of a tadpole’s metamorphosis into an adult frog.
→ In the absence of thyroxin, the tadpole does not transform into an adult and remains in the tadpole stage.
Life cycle of silkworm

→ Silkworm grows on mulberry trees and feeds on its leaves.
→ During a stage in its life cycle, silkworm spins a cocoon around itself.
→ Silk is obtained from this cocoon.
Hormone responsible for metamorphosis in insects
→ In insects, metamorphosis is controlled by the insect hormones. Some of the insect hormones are:
(i) Prothoracicotropic Hormone (PTTH)
(ii) Ecdysone
(iii) Juvenile Hormone (JH)
