Solutions of Life Process Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur HOTS, VSAQ, SAQ and LAQ and Pg No. 28 Class 10 Biology

102. When a person eats sugary food, then organisms A present in his mouth act on sugar to produce a substance B. The substance B first dissolves the calcium salts from the top part C of the tooth and then from its middle part D forming holes E. These holes ultimately reach the part F in the lower part of tooth which contains nerves and blood vessels. The substance B irritates the nerve endings inside the tooth causing toothache.
(a) What are (i) organisms A, and (ii) substance B?
(b) What are (i) part C, and (ii) part D, of tooth known as?
(c) By what name are the holes E in the tooth known?
(d) Name the part F of the tooth.
(e) What will happen if organisms A reach part F of the tooth?
Answer
→ (a) (i) Organisms A ---Bacteria
(ii) Bacteria (A), present in the mouth act on sugar and produce acid (B).
(b) (i) The topmost part of the tooth is enamel
(C). It is the hardest tissue in the body.
(ii) The middle part of the tooth is known as dentine (D).
(c) Dental caries (E) is tooth decay.
(d) The lower part of the tooth is known as pulp cavity (F) which contains nerves and blood vessels.
(e) If bacteria (A) reach the pulp cavity (F) of the tooth it would cause inflammation and infection which would then lead to severe pain.
103. H the teeth are not cleaned regularly, they become covered with a sticky yellowish layer W of food particles and bacteria. Since layer W covers the teeth, the alkaline liquid X secreted by glands Y inside the mouth cannot reach the teeth surface to neutralise the acid formed by the action of organisms Z on sugary food, and hence tooth decay sets in.
(a) What is W known as?
(b) What is (i) X, and (ii) Y?
(c) What are organisms Z?
(d) State one way of removing layer W from the teeth.
Answer
→ (a) W is Dental Plaque. (b) (i) X is Saliva (ii) Y is Salivary Glands. (c) Z are Bacteria. (d) Layer W can be removed by brushing teeth after eating.
104. When a person puts food in his mouth, then teeth cut it into small pieces, chew and grind it. The glands A in the mouth secrete a substance B which is mixed with the food by tongue. The substance B contains an enzyme C which starts the digestion of food in the mouth. The slightly digested food from the mouth goes down a tube D. The special type of movements E in the walls of tube D push the food into stomach for further digestion. The stomach wall secretes gastric juice containing three substance F, G and H. One of the functions of F is to kill bacteria which may enter the stomach with food. The substance G protects the inside layer of stomach from the damaging effect of substance F whereas substance H is an enzyme for digestion. The partially digested food then enters into small intestine for further digestion.
(a) What is (i) gland A
(ii) substance B, and (iii) enzyme C?
(b) Name the tube D.
(c) What is the movement E known as?
(d) What are (i) F (ii) G, and (iii) H?
Answer
→ (a) (i) Salivary glands (A) present in the mouth and secrete saliva.
(ii) Salivary glands(A) secrete saliva (B) which contains an enzyme called salivary amylase (C).
(b) D is Oesophagus. Oesophagus is a long, thin and muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) to the stomach.
(c) Peristaltic movement (E) is a wave of contraction and expansion which occurs in the alimentary canal and helps to push the food forward.
(d) (i) Hydrochloric acid (ii) Mucus (iii) Enzyme pepsin
The stomach wall secretes gastric juice which contains three substances: Hydrochloric acid (F), the enzyme pepsin (G) and mucus (H).
105. The partially digested food coming from the stomach of a person enters a long and narrow organ A in his body. The organ A receives the secretions of two glands : liver and pancreas. Liver secretes a greenish yellow liquid B which is normally stored in the organ C. Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which contains three digestive enzymes D, E and F. The intestinal juice completes the process of digestion of food. The inner wall of organ A has millions of tiny finger-like projections G which help in the rapid absorption of digested food into blood stream. The undigested part of food then passes into wider tube H which absorbs most of the water from undigested food. The last part of tube H called I stores this undigested food (or waste) for some time. The undigested food is then passed out though opening J as faeces in the process known as K.
(a) Name the organ A
(b) Name (t) liquid B, and (it) organ C.
(c) What are the digestive enzymes D, E and F?
(d) Name the projections G present on the inner wall of organ A.
(e) Name (i) tube H (ii) part I (iii) opening J, and (iv) process K.
Answer
→ (a) Small intestine (A).
(b) Bile (B) is a alkaline fluid which is stored in the gall bladder (C).
(c) Pancreatic juice contains three digestive enzymes: Pancreatic amylase (D), Trypsin (E) and Lipase (F).
(d) The inner wall of small intestine (A) has millions of finger-like projections called Villi (G).
(e) (i) The undigested food passes from the small intestine (A) into a wide tube called Large intestine (H).
(ii) The last part of large intestine is Rectum (I).
(iii) The opening by which undigested food is passed out is Anus (J).
(iv) The process by which undigested food is thrown out from the body is Egestion (K).
106. A unicellular animal P having no fixed shape ingests a food particle by forming temporary finger-like projections Q. The food particle is engulfed with a little surrounding water to form a temporary stomach R inside it. The chemicals S from surrounding cytoplasm enter into R and break down food into small and soluble molecules by chemical reactions. The digested food is absorbed directly into cytoplasm by the process T. The undigested food is thrown out of the body by the rupture of a cell organelle U in a process called V.
(a) Name the unicellular animal P. (b) What are (i) Q and (ii) R ?
(c) Name (i) chemicalS, and (ii) process T.
(d) Name (i) organelle U, and (ii) process V.
Answer
→ (a) Amoeba (P) is a unicellular animal which has no mouth for ingestion of food.
(b) (i) Amoeba (P) engulfs the food particles by forming finger-like projections called pseudopodia (Q).
(ii) The food is engulfed with little water to form a food vacuole (R).
(c) (i) Enzymes (S) breaks down food into small soluble molecules.
(ii) The digested food is absorbed directly into the cytoplasm by diffusion (T).
(d) (i) The undigested food is thrown out of the body by rupturing the cell membrane (U) (ii) Egestion (V) is the process of throwing the undigested food out of the body.
107. There are four organisms A, B, C and D. The organism A eats only the flesh of other animals as food. The organism B can eat grains, fruits and vegetables as well as meat and fish. The organism C can make the food itself from simple inorganic substances present in the environment by utilising sunlight energy. On the other hand, organism D eats only plants and their products as food.
(a) Which organism is (i) omnivore
(ii) herbivore, and (iii) carnivore ?
(b) Which organism is an autotroph ?
(c) Which organism is/are heterotroph(s)?
(d) Which organism can be a producer ?
(e) Which organism is/are consumer (s)?
(f) Give one example each of organisms which could be like (i) A (ii) B (iii) C, and (iv) D
Answer
→ (a) (i) B is omnivore. (ii) D is herbivore (iii) A is carnivore.
(b) C is autotroph because it can make its food.
(c) A, B and D are heterotrophs because they cannot make their food.
(d) Organism C can be a producer because it can make own food.
(e) A, B and D are consumers because they cannot make their own food and depend on other organisms for their food.
(f) (i) Tiger (ii) Human beings (iii) Green Plants (iv) Goat
108. The organisms A, B and C can obtain their food in three different ways. Organism A derives its food from the body of another living organism which is called its D, without killing it. The organism B takes in the solid food by the process of ingestion, digests a part of this food and throws out undigested food in the process called E. The organism C obtains its food from dead and decaying plants.
(a) What is the mode of nutrition of
(i) organism A
(ii) organism B, and
(iii) organism C ?
(b) What is the organism like D called ?
(c) Name the process E.
(d) Give one example each of organisms like (i) A (ii) B, and (ii) C.
(e) What is the general name of three modes of nutrition exhibited by organisms A, B and C ?
Answer
→ (a)
(i) The mode of nutrition of organism A is parasitic nutrition.
(ii) The mode of nutrition of organism B is holozoic nutrition.
(iii) The mode of nutrition of organism C is saprophytic nutrition
(b) The organism D is called host of organism A.
(c) The process by which undigested food is thrown out of the body is known as egestion (E).
(d) (i) Plasmodium (ii) Amoeba (iii) Fungi
(e) Heterotrophic nutrition
109. An organism A which cannot move from one place to another, makes a simple food B from the substances C and D available in the environment. This food is made in the presence of a green coloured substance E present in organs F in the presence of light energy in a process called G. Some of the simple food B also gets converted into a complex food H for storage purposes. The food H gives a blue-black colour with dilute iodine solution.
(a) What is (i) organism A (ii) food B, and (iii) food H ?
(b) What are C and D?
(c) Name (i) green coloured substance E, and (ii) organ F.
(d) What is the process G?
Answer
→ (a)
(i) Green plant (A) cannot move from one place to another.
(ii) Green plant makes food glucose (B).
(iii) Glucose (B) gets converted into a complex food, starch (H).
(b) Plant can make own food from the simple substances carbon dioxide (C) and water (D).
(c) Green pigment called chlorophyll (E) present in the leaves of the plant.
(d) The process by which green plants make their own food is called photosynthesis (G).
110. X is a wild animal which eats only the flesh of other animals whereas Y is a domestic animal which feeds mainly on green grass.
(a) What are animals like X known as?
(b) What are animals like Y known as ?
(c) Which animal, X or Y, has a longer small intestine? Why?
(d) Name one animal which is like X.
(e) Name one animal which is like Y.
Answer
→ (a) Carnivores
(b) Herbivores
(c) Animal (Y) has a longer small intestine. Y is an herbivorous animal which eats grass. Grass contains cellulose which is a carbohydrate and gets digested with difficulty. A longer small intestine facilitates complete digestion of cellulose.
(d) Lion
(e) Cow
Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-46
1. Do all cells use oxygen to produce energy?
Answer
→ No, all cells do not use oxygen to produce energy.
2. Name one substance which is produced in anaerobic respiration by an organism but not in aerobic respiration.
Answer
→ Ethanol is the substance that is produced in anaerobic respiration by an organism but not in aerobic respiration.
3. Name one organism which can live without oxygen.
Answer
→ Yeast is an organism which doesn’t utilize oxygen.
4. In which type of respiration, aerobic or anaerobic, more energy is released?
Answer
→ Aerobic respiration produces more energy than anaerobic respiration.
5. Name the substance whose build up in the muscles during vigorous physical exercise may cause cramps.
Answer
→ Lactic acid slowly poison our muscles and cause muscular cramps.
6. Which part of roots is involved in the exchange of respiratory gases?
Answer
→ Root hairs taken up oxygen from the soil and thus get involved in the exchange of respiratory gases.
7. Name the process by which plant parts like roots, stems, and leaves get oxygen required for respiration.
Answer
→ The process by which plant parts like roots, stems, and leaves get oxygen required for respiration is called as diffusion.
8. Name the pores in a leaf through which respiratory exchange of gases takes place.
Answer
→ Stomata present on the surface of the leaves exchange gases for respiration.
9. Name the areas in a woody stem through which respiratory exchange of gases takes place.
Answer
→ Lenticels present on the stem of a plant exchange gases for respiration.
10. What is the name of the extensions of the epidermal cells of a root which help in respiration?
Answer
→ The extensions of the epidermal cells of a root which help in respiration is known as Root Hair.
11. Out of photosynthesis and respiration in plants, which process occurs :
(a) all the time ?
(b) only at daytime ?
Answer
→ (a) Respiration is the process through which plants breathe and it happens all the time.
(b) Photosynthesis happens only during the day time as it requires sunlight.
12. Name the organs of breathing in fish.
Answer
→ The organs with which fish breathe is known as Gills.
13. Name an animal which absorbs oxygen through its moist skin.
Answer
→ Earthworm is the animal which exchanges gases i.e. oxygen through its moist skin.
14. Name an animal which depends on simple diffusion of gases for breathing.
Answer
→ The animal which depends on simple diffusion of gases for breathing is the single-celled Amoeba.
15. Name two animals which breathe through gills.
Answer
→ Two animals which breathe through gills are Prawns and Mussels.
16. The trachea divides into two tubes at its lower end. What is the name of these tubes?
Answer
→ The two tubes at the lower end of trachea are known as Bronchi.
17. Where does the blood absorb oxygen in the human body?
Answer
→ Alveoli of lungs is the place where gaseous exchange take place and blood absorb oxygen in the body.
18. Name the red pigment which carries oxygen in blood.
Answer
→ Haemoglobin is a dark red respiratory pigment that carries oxygen in blood.
19. Which gases are exchanged in your lungs?
Answer
→ Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are the gases which are exchanged inside the lungs.
20. Where in the lungs does gas exchange take place?
Answer
→ Alveoli of lungs is the place where exchange of gases takes place.
21. What is the name of tiny air-sacs at the end of smallest bronchioles in the lungs ?
Answer
→ The tiny air-sacs at the end of the smallest bronchioles are known as Alveoli.
22. What is the other name of wind-pipe?
Answer
→ Wind-pipe is also known as Trachea.
23. What organs are attached to the two bronchi?
Answer
→ On each of the bronchi, lungs are attached.
24. In the lungs:
(a) what substance is taken into the body ?
(b) what substance is removed from the body ?
Answer
→ (a) Inside the lungs, oxygen is taken into the blood.
(b) In the lungs, Carbon Dioxide is taken out from the body.
25. State whether the following statements are true or false :
(a) During respiration, the plants take C02
(b) Energy can be produced in cells without oxygen.
(c) Fish and earthworm exchange gases during respiration in the same way.
Answer
→ (a) False. (b) True. (c) False.
26. Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
(a) The organs of respiration in man are the.................
(b) The actual exchange of gases takes place in the................of the lungs.
(c) ..................in the lungs provide a very large surface area for gaseous exchange.
(d) Yeast undergoes..............respiration whereas Amoeba undergoes..................respiration.
(e) Gills are the breathing organs in................
Answer
→ (a) Lungs.
(b) Alveoli.
(c) Alveoli.
(d) Anaerobic, aerobic.
Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-47
27. Explain why, a land plant may die if its roots remain waterlogged for a long time.
Answer
→ Land plants die if their roots remain waterlogged for a long time because excess of water, in the soils, expels all the air that is present in between the soil particles. Because of the absence of air, oxygen is not available to the roots and they respire anaerobically leading to generation of alcohol which kills the plants.
28. What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use anaerobic mode of respiration.
Answer
Aerobic Respiration
| Anaerobic Respiration |
| Takes Place when oxygen is present. | Takes place when oxygen is not present. |
| Food gets broken down completely. | Food get broken down partially. |
| End products include carbon dioxide and water. | End products include ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast) and lactic acid (in animal muscles). |
| Produces lot of energy. | Produces less energy. |
Some organisms that use anaerobic mode of respiration are Yeast and some bacteria.
29. Name the final product/products obtained in the anaerobic respiration, if it takes place:
(a) in a plant (like yeast).
(b) in an animal tissue (like muscles).
Answer
→ (a) Anaerobic respiration in plants like yeast produces ethanol and carbon dioxide.
(b) Anaerobic respiration in animal tissues like muscles produces lactic acid.
30. What type of respiration takes place in human muscles during vigorous physical exercise? Give reason for your answer.
Answer
→ During vigorous physical exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in human muscles because oxygen is used faster in the muscles compared to its supply by the blood.
31. Name the type of respiration in which the end products are:
(a) C2H50H and C02
(b) C02 and H20
(c) Lactic acid
Give one example of each case where such a respiration can occur.
Answer
→ (a) Anaerobic respiration in yeast produces C2H50H (ethanol) and C02(carbon dioxide)
(b) Aerobic respirations in human beings produces C02(carbon dioxide) and H20 (water).
(c) Anaerobic respiration in animal muscles produces lactic acid.
32. Define breathing. State the differences between breathing and respiration.
Answer
→ Breathing is the process by which organisms takes oxygen from the air and releases carbon dioxide.
Breathing
|
Respiration
|
It is a simple process.
|
It is a complex process.
|
It involves taking oxygen from the air and releasing carbon dioxide in the air.
|
It involves breathing and oxidation of food to release energy.
|
It is a physical process.
|
It is a bio-chemical process.
|
33. What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms? Give one example of each.
Answer
→ Glucose is oxidized, to provide energy in various organisms, in two ways –
i. Aerobic respiration – this respiration process takes place using oxygen. For example, plants and animals oxidize glucose and break it down into carbon dioxide and water to release energy.
ii. Anaerobic respiration – This respiration process takes place in the absence of oxygen. For example, yeast and some bacteria oxidize glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
34. Explain why, when air is taken in and let out during breathing, the lungs always contain a residual volume of air.
Answer
→ During the breathing process when air is taken in and let out, some of the air remains inside the lungs to provide sufficient time for oxygen absorption into the blood and release of carbon dioxide from the blood.
35. Explain why, it is dangerous to inhale air containing carbon monoxide.
Answer
→ Carbon monoxide binds itself strongly with haemoglobin in the blood and prevents it from carrying oxygen to the different parts of the body including brain. Due to this, the person cannot breathe and may even die. Hence, it is dangerous to inhale air containing carbon monoxide.
36. Describe the process of respiration in Amoeba. State whether it is anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration.
Answer
→ Respiration happens in amoeba through simple diffusion of gases. It lives in water which contains dissolved oxygen. The diffusion of gases takes place through its cell membrane. Through its thin cell membrane this oxygen diffuses into the body of amoeba and spreads into the whole body. This oxygen is used for respiration inside the Amoeba cell. The process of respiration produces carbon dioxide which diffuses out again through its thin cell membrane.
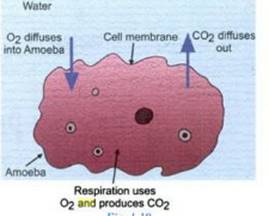
Figure to show the process of breathing (gaseous exchange) in Amoeba
It is an aerobic respiration.
37. State the three common features of 'all the respiratory organs like skin, gills and lungs.
Answer
→ The three common features of all respiratory organs like skin, gills and lungs are as follows:
i) They have a large surface area to absorb sufficient amount of oxygen.
ii) They have thin walls which makes diffusion and exchange of gases easier.
iii) All respiratory organs like skin, gills and lungs have a rich blood supply for the transportation of respiratory gases.
38. Describe the process of respiration in fish.
Answer
→ The respiratory organ in a fish is called as gills which is covered by gill covers. The fish has gills on both sides of its head. Fish live in water containing dissolved oxygen. During the process of respiration, fish takes in the water through its mouth and passes it over the gills. The gills extract the oxygen, dissolved in the water, and send it to all the parts of the fish through blood. The carbon dioxide produced during respiration is carried by the blood to the gills where it is expelled into the surrounding water.

Figure to show the process of breathing in fish.
39. What would be the consequences of deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer
→ The haemoglobin present in the blood is responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood. Thus the deficiency of haemoglobin will reduce the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood resulting in tiredness, breathing problems and lack of energy.
40. Describe the process of respiration in the following parts of a plant:
(a) Root (b) Stem (c) Leaves
Answer
→ (a) The epidermal cells of a root have extensions which are known as root hairs. These root hairs are in contact with the soil and the air present in between the soil particles diffuses through these root hairs to reach all other cells of the root for respiration. Carbon dioxide produced by the cells during the respiration reaches the root hairs and moves out through the process of diffusion. Hence, respiration in roots happens by diffusion of respiratory gases through root hairs.
(b) The stems of herbaceous plants have stomata through which oxygen diffuses into the stem and reaches all the cells for respiration. The carbon dioxide produced during respiration diffuses out the stomata. In woody stems, respiration happens through lenticels present in the bark.
(c) Leaves of a plant have tiny pores called stomata. Oxygen, present in the air, diffuses through these stomata and reaches other cells for respiration. Carbon dioxide produced in the cells during respiration also diffuses out through these stomata.
41A. What is meant by aquatic animals and terrestrial animals ?
Answer
→ The animals which live in water are aquatic animals and animals which live on land are terrestrial animals.
41B. From where do the aquatic animals and terrestrial animals obtain oxygen for breathing and respiration ?
Answer
→ Aquatic animals utilize the oxygen present in the water for respiration while terrestrial animals take oxygen from the air.
42. Why do fishes die when taken out of water?
Answer
→ Fishes do not have lungs which can take oxygen from air. Hence, they die when taken out of water. They have gills which can only take oxygen dissolved in water.
43. Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Answer
→ The oxygen content of water is much less than the oxygen content of air and hence rate of breathing is aquatic organisms is faster than in terrestrial organisms.
44. Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
Answer
→ The energy currency in the living organisms is called as “ATP”. During anaerobic respiration in lower organisms, it is produced in cytoplasm while in higher organisms, which respire aerobically, it is produced in mitochondria.
45. Explain why, plants have low energy needs as compared to animals.
Answer
→ Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals because they do not move. Moreover, in a large plants there are many dead cells like sclerenchyma because of which they also need less energy.
46. Explain how, it would benefit deep sea divers if humans also had gills.
Answer
→ If humans also had gills, deep sea divers could remain under the sea for a longer time without using oxygen cylinders as gills would extract the oxygen, dissolved in water, for breathing.
Long Answer Type Questions-Pg-48
47A. What is the function of the respiratory system?
Answer
→ The primary function of respiratory system is to inhale oxygen, which is then used to digest food and produce energy, and exhale carbon dioxide.
47B. What are the major organs of respiratory system in man (or humans)?
Answer
→ The major organs of respiratory system in humans are: Nose, Nasal Passage, Trachea (wind pipe), Bronchi, Lungs and diaphragm.
47C. Draw a labelled diagram of the human respiratory system.
Answer
→ Human Respiratory System:

48A. Explain how, the air we breathe in gets cleaned while passing through the nasal passage.
Answer
→ The inner lining of nostril is lined by nasal hair and remains wet due to mucus secretion. When air passes through the nasal passage, the nasal hair and mucus trap the dust particles and other impurities present in the inhaled air. Thus, clean air goes into the lungs.
48B. Why do the walls of trachea not collapse when there is less air in it?
Answer
→ The walls of trachea do not collapse when there is no air in it because they are supported by rings of cartilage.
48C. How are oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged in our body during respiration?
Answer
→ When we breath in, the air sacs or alveoli get filled with air containing oxygen. The alveoli are surrounded by thin blood vessels called capillaries carrying blood in them. So, the oxygen of air diffuses out from the alveoli into the blood. Blood carries this oxygen to all the parts of the body. When it passes through the tissues, the oxygen in the blood diffuses into the cells and mixes with the digested food to release energy. Carbon dioxide produced during respiration in the cells diffuses into the blood which is carried to the lungs. Inside the lungs, the carbon dioxide diffuses into the alveoli.
48D. How are lungs designed in human beings to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer
→ To maximize the exchange of gases, lungs have millions of alveoli which provides a larger surface area for the exchange of gases.
49A. Give the main points of difference between respiration in plants and respiration in animals.
Answer
Respiration in Plants
|
Respiration in Animals
|
It doesn’t have specialized organ for respiration. All the parts of the plants perform respiration individually.
|
In animals, respiration occurs through specialized organs like lungs, gills, etc.
|
There is a little transport of respiratory gases from one part of the plant to the other during respiration.
|
Respiratory gases are usually transported over long distances inside an animal during respiration.
|
The rate of respiration is slow.
|
The rate of respiration is fast.
|
49B. Describe the exchange of gases which takes place in the leaves of a plant (a) during daytime, and (b) at night.
Answer
→ (i) During the daytime, plants carry out both photosynthesis and respiration. During photosynthesis, oxygen is produced some of which is used by the plant leaves and rest is released into the air. During respiration, carbon dioxide is produced which is entirely utilized by leaves for photosynthesis. Leaves even absorb more carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis. Thus during the day time, the exchange of gases looks like : Oxygen diffuses out and carbon dioxide diffuses in.
(ii) During the night, photosynthesis doesn’t take place and hence only respiration process occurs in plants. Because of the absence of photosynthesis, oxygen is not produced. For respiration, leaves take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide into the air. Thus during the night time, the exchange of gases looks like : Oxygen diffuses in and carbon dioxide diffuses out.
49C. Which contains more carbon dixoide: exhaled air or inhaled air? Why?
Answer
→ In the exhaled air, carbon dioxide content is always more than inhaled air because during the respiration process, oxygen breaks down the glucose and generates carbon dioxide which passes out of the body in the exhaled air.
50A. "Respiration is a vital function of the body". Justify this statement.
Answer
→ Respiration is a vital function of the body as it provides energy for carrying out biological functions which are essential for survival and maintenance of an organism.
50B. What is the main difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration? Give one example of each.
Answer
Aerobic Respiration
|
Anaerobic Respiration
|
Takes Place when oxygen is present.
|
Takes place when oxygen is not present.
|
Food gets broken down completely.
|
Food get broken down partially.
|
End products include carbon dioxide and water.
|
End products include ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast) and lactic acid (in animal muscles).
|
Produces lot of energy.
|
Produces less energy.
|
Example: Human beings
|
Example: Yeast
|
50C. What type of respiration takes place (i) in yeast, and (ii) in humans ?
Answer
→ In yeast- Anaerobic respiration
In humans-Aerobic respiration
51A. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of large multicellular organisms like humans?
Answer
→ Large multicellular organisms like humans cannot depend on diffusion to meet the oxygen requirements as the volume is too big and oxygen cannot diffuse into all the cells quickly. Moreover, in order to reach each and every cell of the human body, oxygen will have to travel a large distance.
51B. What type of arrangement exists in the bodies of large animals to meet their oxygen requirements adequately?
Answer
→ Large organisms have oxygen carrying pigments, called haemoglobin, in the blood, which carries the oxygen from the lungs to different parts of the body.
51C. What advantage a terrestrial animal has over an aquatic animal with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer
→ The advantage that terrestrial animals have over an aquatic animal is that terrestrial animals live in an oxygen rich environment from where they can take as much oxygen as they want.
