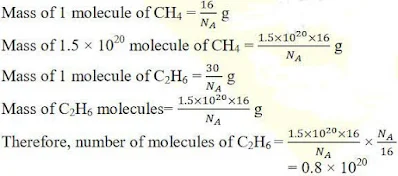NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Solutions
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules covers all the important questions and answers as well as advanced level questions. It helps in learning about the Atom and its size, characteristics, modern symbols of atoms, Law of Conservation of mass, chemical symbols, valency, cation, anion, solubility of substances and molecules.
The NCERT Exemplar solutions for class 9 science is very important in the examination. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules is provided by our experts. They prepared the best solutions which help the students in understanding the solutions in an easy way. This chapters also covers the other topics like bonding, molecule of elements, molecules of compounds, ions and writing formula for the compound.
Chapter Name | Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules |
Book Title | NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science |
Related Study |
|
Topics Covered |
|
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Science
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following correctly represents 360 g of water?
(i) 2 moles of H2O
(ii) 20 moles of water
(iii) 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
(iv) 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
(a) (i)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Solution
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Number of moles = Mass of water/Molar mass of water
Number of moles = 360/120 = 20
Number of molecules = 20 ×6.022× 1023
= 1.2044 ×1025 molecules of water
2. Which of the following statements is not true about an atom?
(a) Atoms are not able to exist independently.
(b) Atoms are the basic units from which molecules and ions are formed.
(c) Atoms are always neutral in nature.
(d) Atoms aggregate in large numbers to form the matter that we can see, feel or touch.
Solution
(a) Atoms are not able to exist independently.
3. The chemical symbol for nitrogen gas is :
(a) Ni
(b) N2
(c) N+
(d) N
Solution
(b) N2
Chemical formula of Nitrogen is N but nitrogen exist as a molecule of two atoms. Therefore, the chemical symbol of nitrogen gas is N2.4. The chemical symbol for sodium is :
(a) So
(b) Sd
(c) NA
(d) Na
Solution
(d) Na
Sodium word is derived from Latin word Natrium hence the chemical name of sodium is Na.
5. Which of the following would weigh the highest?
(a) 0.2 mole of sucrose (C12 H22 O11)
(b) 2 moles of CO2
(c) 2 moles of CaCO3
(d) 10 moles of H2O
Solution
(c) 2 moles of CaCO3
Weight of a sample in grant = Number of moles ×Molar mass
(a) 0.2 moles of C12H22O11= 0.2 ×342 = 68.4 g
(b) 2 moles of CO2is 2 × 44 = 88 g
(c) 2 moles of CaCO3= 2 ×100=200 g
(d) 10 moles of H2O= 10 ×18 = 180g
6. Which of the following has maximum number of atoms ?
(a) 18g of H2O
(b) 18g of O2
(c) 18g of CO2
(d) 18 g of CH4
Solution
(d) 18 g of CH4
7. Which of the following contains maximum number of molecules ?
(a) 1 g CO2
(b) 1 g N2
(c) 1 g H2
(d) 1 g CH4
Solution
(c) 1 g H2
1 g of H2 = ½ ×NA
= 0.5 NA
= 0.5 × 6.022 × 1023
= 3.011 × 1023
8. Mass of one atom of oxygen is :
(a) 16/(6.023 × 1023 g)
(b) 32/(6.023 × 1023 g)
(c) 1/(6.023 × 1023 g)
(d) 8u
Solution
(a) 16/(6.023 ×1023 g)
Mass of one atom of oxygen = Atomic mass/NA
= 16/6.023× 1023 g
9. 3.42 g of sucrose are dissolved in 18 g of water in a beaker. The number of oxygen atoms in the solution are :
(a) 6.68 × 1023
(b) 6.09 × 1022
(c) 6.022 × 1023
(d) 6.022 × 1021
Solution
(a) 6.68 × 1023
1 mol of sucrose (C12H22O11) contains = 11× NA atoms of oxygen,
Here, NA= 6.023×1023
0.01 mol of sucrose (C12H22O11) contains = 0.01 × 11 × NA atoms of oxygen
= 0.11× NA atoms of oxygen
= 18 g/(1×2+ 16)gmol-1
= 1mol
1mol of water (H2O) contains 1× NA atom of oxygen
Total number of oxygen atoms = Number of oxygen atoms from sucrose + Number of oxygen atoms from water
= 0.11 NA + 1.0 NA = 1.11NA
Number of oxygen atoms in solution = 1.11 × Avogadro’s number
= 1.11 × 6.022 ×1023
= 6.68 × 1023
10. A change in the physical state can be brought about :
(a) Only when energy is given to the system.
(b) Only when energy is taken out from the system.
(c) When energy is either given to, or taken out from the system.
(d) Without any energy change.
Solution
(c) When energy is either given to, or taken out from the system.
Short Answer Questions
11. Which of the following represents a correct chemical formula? Name it.
(a) CaCl
(b) BiPO4
(c) NaSO4
(d) NaS
Solution
(a) CaCl = Wrong (valency of Ca = 2, Cl = 1)
(b) BiPO4 = Correct (valency of Bi = 3, PO4 = 3)
(c) NaSO4 = Wrong (valency of Na = 1, SO4 = 2)
(d) NaS = Wrong (valency of Na = 1, Sulphide = 2)
Bismuth phosphate is right because both ions are trivalent.
12. Write the molecular formulae for the following compounds.
Solution
(a) Copper (II) bromide = CuBr2
(b) Aluminium (III) nitrate = Al(NO3)3
(c) Calcium (II) phosphate = Ca3(PO4)2
(d) Iron (III) sulphide = Fe2S3
(e) Mercury (II) chloride = HgCl2
(f) Magnesium (II) acetate = Mg(CH3COO)2
13. Write the molecular formulae of all the compounds that can be formed by the combination of given ions : Cu3+, Na+, Fe3+, Cl, SO34 PO43 .
Solution
CuCl2/CuSO4/Cu3(PO4)
NaCl/Na2SO4/Na3PO4
FeCl3/Fe(SO4)3/FePO4
14. Write the cations and anions present (if any) in the following compounds :
(a) CH3COONa
(b) NaCl
(c) H2
(d) NH4NO3
Solution
Compounds | Cations | Anions |
CH3COONa | Na+ | CH3COO |
NaCl | Na+ | Cl |
H2 | Nil | Nil |
NH4NO3 | NH4+ | NO3 |
Solution
(a) Calcium and fluoride -Calcium Fluoride (CaF2)
(b) Hydrogen and sulphur-Hydrogen Sulphide(H2S)
(c) Nitrogen and hydrogen-Ammonia(NH3)
(d) Carbon and chlorine -Carbon Tetrachloride(CCl4)
(e) Sodium and oxygen -Sodium Oxide(Na2O)
(f) Carbon and oxygen-Carbon dioxide(CO2); Carbon Monoxide(CO)
16. Which of the following symbols of elements are incorrect? Give their correct symbols
(a) Cobalt CO
(b) Carbon c
(c) Aluminium AL
(d) Helium He
(e) Sodium So
Solution
(a) Incorrect, the correct symbol of cobalt is Co
(b) Incorrect, the correct symbol of carbon is C
(c) Incorrect, the correct symbol of aluminium is Al
(d) Correct (He)
(e) Incorrect, the correct symbol of sodium is Na
17. Give the chemical formulae for the following compounds and compute the ratio by mass of the combining elements in each one of them.
(a) Ammonia
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Hydrogen chloride
(d) Aluminium fluoride
(e) Magnesium sulphide
Solution
(a) NH3 | (b) CO | (c) HCl | (d) AlF3 | (e) MgS |
N : H × 3 | C : O | H : Cl | Al : F × 3 | Mg : S |
14 : 1 × 3 | 12 : 16 | 1 : 35.5 | 27 : 19 × 3 | 24 : 32 |
14 : 3 | 3 : 4 | 1 : 35.5 | 9 : 19 | 3 : 4 |
18. State the number of atoms present in each of the following chemical species.
(a) CO2-3
(b) PO3-4
(c) P2O5
(d) CO
Solution
(a) | CO2-3 | 1 + 3 = 4 |
(b) | PO3-4 | 1 + 4 = 5 |
(c) | P2O5 | 2 + 5 = 7 |
(d) | CO | 1 + 1 = 2 |
19. What is the fraction of the mass of water due to neutrons?
Solution
- Mass of 1 molecule of water = 18 amu
- No. of proton in 2 atoms of H = 2 and no. of neutron = 0
- No. of proton in 1 atom of O = 8 and no. of neutron = 8
- Fraction of mass due to neutron in water 8/18 = 4/9
20. Does the solubility of a substance change with temperature? Explain with the help of an example.
Solution
Yes, the solubility of a substance depends on its temperature. The solubility generally, increases with an increase in temperature.
For example: one can dissolve more sugar in hot water than in cold water.
21. Classify each of the following on the basis of their atomicity.
(a) F2(b) NO2
(c) N2O
(d) C2H6
(e) P4
(f) H2O2
(g) P4O10
(h) O3
(i) HCl
(j) CH4
(k) He
(l) Ag
(a) Diatomic (2 atoms)
(b) Triatomic (3 atoms)
(c) Triatomic (3 atoms)
(d) Polyatomic (8 atoms)
(e) Polyatomic (4 atoms)
(f) Polyatomic (4 atoms)
(g) Polyatomic (14 atoms)
(h) Triatomic (3 atoms)
(i) Diatomic (2 atoms)
(j) Polyatomic (5 atoms)
(k) Monoatomic (1 atom)
(l) Monoatomic(1 atom)
22. You are provided with a fine white coloured powder which is either sugar or salt. How would you identify it without tasting?
Solution
We can identify the powder by heating. The powder will char if it is a sugar. Alternatively, the powder can be dissolved in water and checked for electrical conductivity. If it conducts, then the powder is salt.
23. Calculate the number of moles of magnesium present in a magnesium ribbon weighing 12 g. Molar atomic mass of magnesium is 24gmol–1.
Solution
Long Answer Questions
24. Verify by calculating that :
(a) 5 moles of CO2 and 5 moles of H2O do not have the same mass.
(b) 240 g of calcium and 240 g of magnesium elements have a mole ratio of 3 : 5.
Solution
(a) CO2 has molar mass = 44 g mol–1
5 moles of CO2 have molar mass = 44 × 5 = 220 g
H2O has molar mass = 18 g mol-1
5 moles of H2O have mass = 18 × 5g= 90 g
(b) Number of moles in 240 g Ca metal 240/40 = 6
Number of moles in 240 g of Mg metal 24 = 240/24 = 10
Ratio, 6 : 10 = 3 : 5
25. Find the ratio by mass of the combining elements in the following compounds :
(a) CaCO3
(b) MgCl2
(c) H2SO4
(d) C2H3OH
(e) NH3
(f) Ca(OH)2
Solution
(a) CaCO3
Ca : C : O × 3
40 : 12 : 16 × 3
40 : 12 : 48
10 : 3 : 12
(b) MgCl2
Mg : Cl × 2
24 : 35.5 × 2
24 : 71
(c) H2SO4
H × 2 : S : O × 4
1 × 2 : 32 : 16 × 4
2 : 32 : 64
1 : 16 : 32
(d) C2H5OH
C × 2 : H × 6 : O
12 × 2 : 1 × 6 : 16
24 : 6 : 16
12 : 3 : 8
(e) NH3
N : H × 3
14 : 1 × 3
14 : 3
(f) Ca(OH)2
Ca : O × 2 : H × 2
40: 16 × 2 : 1 × 2
40 : 32 : 2
26. Calcium chloride when dissolved in according to the following equation :
CaCl2(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2Cl(aq)
Calculate the number of ions obtained from CaCl2 when 222 g of it is dissolved in water.
Solution
1 mole of calcium chloride = 111 g
∴ 222 g of CaCl2 is equivalent to 2 moles of CaCl2
Since 1 formula unit CaCl3 gives 3 ions, therefore, 1 mol of CaCl2 will give 3 moles of ions.
2 moles of CaCl2 would give 3 × 2 = 6 moles of ions
No. of ions = No. of moles of ions × Avogadro number
= 6 × 6.022 × 1023
= 36.132 × 1023 = 3.6132 × 1024 ions
27. The difference in the mass of 100 moles each of sodium atoms and sodium ions is 5.48002 g. Compute the mass of an electron.
Solution
A sodium atom and ion, differ by one electron. For 100 moles each of sodium atoms and ions there would be a difference of 100 moles of electrons.
Mass of 100 moles of electrons= 5.48002 g
28. Cinnabar (HgS) is a prominent ore of mercury. How many grams of mercury are present in 225 g of pure HgS ? Molar mass of Hg and S are 200.6 g mol-1 and 32 g mol-1 respectively.
Solution
Molar mass of HgS = 200.6 + 32 = 323.6 g mol-1
Mass of Hg in 232.6 g of HgS 200.6 g
29. The mass of one steel screw is 4.11g. Find the mass of one mole of these steel screws. Compare this value with the mass of the Earth (5.98 × 1024kg). Which one of the two is heavier and by how many times?
Solution
One mole of screws weigh = 2.475 ×1024g
= 2.475×1021 kg
Mass of earth is 2.4×103 times the mass of screws.
The earth is 2400 times heavier than one mole of screws.
30. A sample of vitamin C is known to contain 2.58 × 1024 oxygen atoms. How many moles of oxygen atoms are present in the sample?
Solution
1 mole of oxygen atoms = 6.022 × 1023 atoms
Number of moles of oxygen atoms
31. Raunak took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container arid Krish also took 5 moles of a sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
(a) Whose container is heavier ?
(b) Whose countainer has more number of atoms ?
Solution
(a) Mass of sodium atoms carried by Krish
= (5 × 23) g = 115 g
While mass of carbon atom carried by Raunak
= (5 × 12) g = 60 g
Thus, Krish’s container is heavy.
(b) As the two bags have the same number of moles of atoms, both the bags will have the same number of atoms.
32. Fill in the missing data in the table :
Species property | Water | CO2 | Na – Atom | MgCl2 |
No. of moles | 2 | ……… | ……… | 0.5 |
No. of particles | ……. | 3.011 × 1023 | …….. | …….. |
Mass | 36 g | …….. | 115 g | …… |
Solution
Species property | Water | CO2 | Na – Atom | MgCl2 |
No. of moles | 2 | 0.5 mole | 5 moles | 0.5 |
No. of particles | 2×6.022×1023 | 3.011×1023 | 5×6.022×1023 | 0.5×6.022×1023×3 |
Mass | 36 g | 22 g | 115 g | 47.5 g |
33. The visible universe is estimated to contain 1022 stars. How many moles of stars are present in the visible universe?
Solution
34. What is the SI prefix for each of the following multiples and submultiples of a unit?
(a) | 103 | (b) | 10-3 |
(c) | 10-2 | (d) | 10-6 |
(e) | 10-9 | (f) | 10-19 |
Solution
(a) | kilo | (b) | deci |
(c) | centi | (d) | micro |
(e) | nano | (f) | pico |
35. Express each of the following in kilograms :
(a) 5.84 × 10–3 mg
(b) 58.34 g
(c) 0.584 g
(d) 5.873 × 10–21 g
Solution
(a) 5.84 × 10–9 kg
(b) 5.834 × 10–2 kg
(c) 5.84 × 10–4 kg
(d) 5.873 × 10–24 kg
36. Compute the difference in masses of 103moles each of magnesium atoms and magnesium ions. (Mass of an electron = 9.1×10–31 kg).
Solution
A Mg2+ion and Mg atom differ by two electrons.
103moles of Mg2+and Mg atoms would differ by 103× 2 moles of electrons.
Mass of 2 ×103moles of electrons = 2×103× 6.023×1023×9.1×10–31kg
=2×6.022 × 9.1×10–5kg
=109.6004 ×10–5kg
=1.096 × 10–3kg
37. Which has more number of atoms?
100 g of N2 or 100 g of NH3
Solution
(i) 100 g of N2 = 100/28 moles
Number of molecules = 100/28 × 6.022 × 1023
Number of atoms = 2 × 100/28 × 6.022 × 1023
= 43.01 × 1023
(ii) 100 g of NH3 = 100/17 moles
= 100/17 × 6.022 × 1023 molecules
= 100/17 × 6.022 × 1023 × 4 atoms
= 141.69 × 1023
∴ NH3 would have more atoms.
38. Compute the number of ions present in 5.85 g of sodium chloride.
Solution
5.85 g of NaCl = 5.85/58.5 = 0.1 mole
or 0.1 mole of NaCl particle.
Each NaCl particle is equivalent to one Na+ one Cl- = 2 ions
Total moles of ions = 0.1 × 2 = 0.2 mole
No. of ions = 0.2 × 6.022 × 1023
= 1.2042 × 1023 ions
39. A gold sample contains 90% of gold and the rest copper. How many atoms of gold are present in one gram of this sample of gold?
Solution
One gram of gold sample will contain = 90/100 = 0.9 g of gold
Number of moles of gold = Mass of gold/Atomic mass of gld
= 0.9/197 = 0.0046
One mole of gold contians Na atoms = 6.022 × 1023
∴ 0.0046 mole of gold will contain = 0.0046 × 6.022 × 1023
= 2.77 × 1021
40. What are ionic and molecular compounds? Give examples.
Solution
While forming some compounds, atoms may gain or lose electrons, thereby forming electrically charged particles called ions. Compounds that are formed by the attraction of cations and anions are known as ionic compounds.
Example: 2Na + Cl2→ 2Na+ Cl-→ 2NaCl (sodium chloride-common salt.)
Compounds formed by the bonding of uncharged species are known as molecular compounds. The bonding is called covalent bonding. Molecular compounds are formed by sharing of electrons between the two atoms.
Example: 2C + O2→ 2CO (Carbon monoxide)
41. Compute the difference in masses of one mole each of aluminium atoms and one mole of its ions (mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10–28 g). Which one is heavier?
Solution
Mass of 1 mole of aluminium atom = the molar mass of aluminium = 27 g mol–1
An aluminium atom needs to lose three electrons to become an ion, Al3+
For one mole of Al3+ ion, three moles of electrons are to be lost.
The mass of three moles of electrons
= 3 × (9.1 × 10-28) × 6.022 × 1023 g
= 27.3 × 6.022 × 10-5 g
= 164.400 × 10-5 g = 0.00164 g
Molar mass of Al3+ = (27 – 0.00164) g mol-1
= 26.9984 g mol-1
Difference = 27 – 26.9984 = 0.0016 g
42. A silver ornament of mass ‘m’ gram is polished with gold equivalent to 1% of the mass of silver. Compute the ratio of the number of atoms of gold and silver in the ornament.
Solution
Mass of silver = mg
Mass of gold = m/100 g
Number of atoms of silver = [Mass/(Atomic mass)] × NA
= m/108 × NA
Number of atoms of gold = (m/100) × 197 × NA
Ratio of number of atoms of gold to silver = An : Ag
= 108 : 19700 = 1 : 182.41
43. A sample of ethane (C2H6) gas has the same mass as 1.5 ×1020 molecules of methane (CH4). How many C2H6 molecules does the sample of gas contain?
Solution
44. Fill in the blanks :
(a) In a chemical reaction, the sum of the masses of the reactants and products remains unchanged.
This is called _____.
(b) A group of atoms carrying a fixed charge on them is called _____.
(c) The formula unit mass of Ca3(PO4)2 is _____.
(d) Formula of sodium carbonate is _____ and that of ammonium sulphate is _____.
Solution
(a) Law of conservation of mass
(b) Polyatomic ion
(c) (3 × atomic mass of Ca) + (2 × atomic mass of phosphorus) + (8 × atomic mass of oxygen) = 310
(d) Na2CO3: (NH4)2SO4
|
Across |
Down |
|
The element used by Rutherford during his α–scattering experiment |
A white lustrous metal used for making ornaments and which tends to get tarnished black in the presence of moist air. |
|
An element which forms rust on exposure to moist air |
Both brass and bronze are alloys of the element |
|
A very reactive non–metal stored under water |
The metal which exists in the liquid state at room temperature |
|
Zinc metal when treated with dilute hydrochloric acid produces a gas of this element which when tested with burning splinter produces a pop sound. |
An element with symbol Pb |
Answer
46. Write the formulae for the following and calculate the molecular mass for each one of them :
(a) Caustic potash
(b) Baking powder
(c) Limestone
(d) Caustic soda
(e) Ethanol
(f) Common salt
Solution
(a) KOH = (39 + 16 + 1) = 56 g mol–1
(b) NaHCO3 = 23 + 1 + 12 + (3 × 16) = 84 g mol–1
(c) CaCO3 = 40 + 12 + (3 × 16) = 100 g mol–1
(d) NaOH = 23 + 16 + 1 = 40 g mol–1
(e) C2H5OH = C2H6O = 2 × 12 + (6 × 1) + 16 = 46 g mol–1
(f) NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5 g mol–1
47. In photosynthesis, 6 molecules of carbon dioxide combine with an equal number of water molecules through a complex series of reactions to give a molecule of glucose having a molecular formula C6H12O6. How many grams of water would be required to produce 18 g of glucose? Compute the volume of water so consumed, assuming the density of water to be 1 g cm–3.
Solution
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
1 mole of glucose needs 6 moles of water.
180 g of glucose needs (6×18) g of water.
1 g of glucose will need 108/180 g of water.
18 g of glucose would need 108/180 × 18 g of water = 10.8 g
Volume of water used = Mass/Density
= 10.8 g/1 g cm-3
= 10.8 cm3